Gaucher disease causes
Last updated April 11, 2025, by Marisa Wexler, MS

Gaucher disease is a rare inherited disorder caused by genetic mutations that interfere with the body’s ability to produce an enzyme needed to break down certain fatty molecules inside cells.
The disease is driven by the abnormal accumulation of these molecules inside specific organs and tissues, which ultimately causes Gaucher disease symptoms such as an enlarged spleen, low blood counts, excessive bleeding, and bone problems.
The standard Gaucher disease treatment to help manage most clinical symptoms include enzyme replacement therapy and substrate reduction therapy.
What causes Gaucher disease?
The exact causes of Gaucher disease are mutations in a gene called GBA1. This gene provides instructions for making the enzyme glucocerebrosidase (GCase), also sometimes referred to as glucosylceramidase or acid beta-glucosidase.
GCase plays an essential role in the normal function of lysosomes, which are cellular compartments that serve as waste disposal systems, helping to break down and recycle molecules that cells no longer need. Specifically, the enzyme helps to degrade glucocerebroside (Gb1) — a fatty molecule also called glucosylceramide — into smaller components that can be reused.
In Gaucher disease, GCase is either missing or not working as it should, so Gb1 accumulates inside cells, thereby driving disease symptoms.
The main cells affected by Gaucher disease are immune cells called macrophages. The word macrophage comes from the Greek, meaning “big eater,” reflecting their role as the body’s sanitation workers. These cells patrol the body, engulfing and digesting foreign pathogens, damaged cells, and molecular debris.
Because macrophages handle large amounts of cellular waste, they contain many lysosomes, which help digest and recycle Gb1 and other engulfed molecules. However, in Gaucher disease, macrophages cannot effectively dispose of Gb1, which accumulates inside their lysosomes, causing these cells to swell and to take on a distinctive “crumpled tissue paper” appearance under a microscope.
These Gb1-laden macrophages, known as Gaucher cells, are the main drivers of disease symptoms in Gaucher disease. Gaucher cells accumulate in a variety of organs, including the spleen and liver, causing these organs to enlarge and triggering inappropriate immune responses that result in inflammation and cell death.
They also accumulate in the bone marrow, leading to problems with the normal production of blood cells. These bone marrow issues, in combination with problems in the spleen, an organ that normally stores and recycles blood cells, leads to the low blood cell counts and bleeding disorders experienced by most Gaucher patients.
When Gaucher cells infiltrate the bone marrow, they also interfere with the blood vessels that supply nutrients and oxygen to bone tissue, leading to bone problems.
While the spleen, liver, and bones are primarily affected in Gaucher disease patients, up to 10% of patients will also experience neurological symptoms.
The mechanisms that drive neurological symptoms in Gaucher disease remain poorly understood, however. There’s some evidence that Gb1 might build up to toxic levels in nerve cells in some patients, but it remains unclear why this seems to affect only some people with the disease.
Can mutations predict symptom severity or disease type?
Gaucher disease is divided into three main types based on the presence and severity of neurological symptoms. The most common form, Gaucher disease type 1, does not cause neurological symptoms, while types 2 and 3 are characterized by severe and milder neurological symptoms, respectively.
More than 400 mutations have been identified as Gaucher disease causes, but predicting a person’s disease type or how their disease will progress based solely on their genetic mutations remains challenging. This is because no clear connection has been found between GCase activity levels and disease severity or type. Even patients with the same mutations can experience significantly different symptoms, likely due to other genetic and environmental factors that are not yet fully understood.
Still, researchers have identified certain GBA1 mutations that tend to be associated with specific disease patterns. These are known as genotype-phenotype correlations and can provide some insight into how the disease might manifest in a given person.
- People with at least one copy of a mutation called p.Asn409Ser almost always have Gaucher disease type 1.
- People with two copies of the p.Asn409Ser mutation, or two copies of another mutation called p.Arg535His, tend to have very mild disease and may not experience any noticeable symptoms.
- People carrying a mutation called p.Leu483Pro often have Gaucher disease type 2 or 3.
- People with two copies of a specific mutation called p.Asp448His develop Gaucher disease type 3c, also called cardiovascular Gaucher disease, which is a specific subtype that’s marked by heart damage and other cardiovascular problems.
- People with perinatal lethal Gaucher disease, a rare subtype of type 2 that causes death before or soon after birth, may have GBA1 mutations that completely disrupt the gene, leading to undetectable GCase enzyme activity.
With few exceptions, these correlations are mostly trends, and it is not always possible to predict someone’s disease type based only on the specific mutations the person carries. For example, although the p.Leu483Pro mutation is common in Gaucher disease types 2 and 3, it has also been reported in people with type 1.
Emerging evidence suggests mutations in other genes and epigenetics — chemical modifications to the DNA, influenced by environmental and behavioral factors, that impact gene activity — may modify GCase activity and contribute to varying disease symptoms in people with the same mutations.
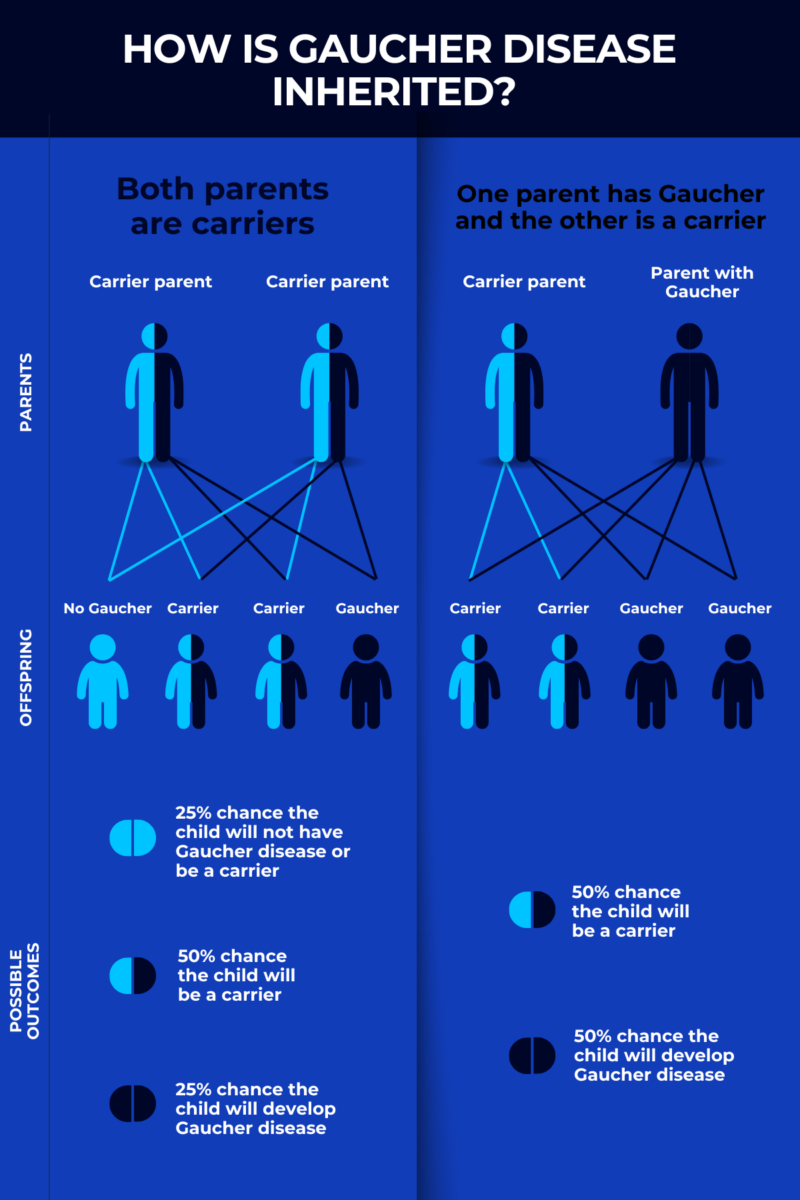
How is Gaucher disease inherited?
Everyone inherits two copies of the GBA1 gene, one from each biological parent. Gaucher disease inheritance follows an autosomal recessive pattern, meaning the disease will only develop if both inherited GBA1 copies are mutated.
People with one mutated copy of the GBA1 gene and a second healthy copy are referred to as disease carriers. These individuals will not develop any symptoms, but they may pass on the mutated gene to their biological children.
Based on the inheritance pattern of Gaucher disease, if two carriers reproduce, there is a:
- 25% chance their child will have Gaucher disease
- 50% chance their child will be a carrier
- 25% chance their child will not have Gaucher disease nor be a carrier.
If a carrier reproduces with someone who has Gaucher disease, there is a:
- 50% chance their child will have Gaucher disease
- 50% chance their child will be a carrier.
If a carrier reproduces with a non-carrier, there is a:
- 50% chance their child will be a carrier
- 50% chance their child will not have Gaucher disease nor be a carrier.
If someone with Gaucher disease reproduces with a non-carrier, then all of their children will be carriers. Finally, two people with Gaucher disease will have biological children who also have the disease.
Of note, it is possible for parents with one Gaucher disease type to have children with a different type. For example, there have been reports of someone with type 1 Gaucher disease having a child with type 2 disease with severe neurological symptoms.
Gaucher disease risk factors
Gaucher disease is a genetic disorder caused by mutations that are present from the moment of conception. Therefore, factors like lifestyle and environmental exposures cannot cause Gaucher disease, though they may influence how an individual experiences symptoms.
Because it is caused by inherited mutations, the only true Gaucher disease risk factor is having biological parents who have Gaucher disease or are carriers of the disease.
However, there are populations where disease mutations occur more frequently than in others. For example, about 6% of the Ashkenazi (Eastern European) Jews are estimated to be carriers of GBA1 mutations, compared with a carrier frequency lower than 1% in non-Jewish populations.
The global Gaucher disease prevalence is about 1.5 per 100,000 live births. In other words, for every 100,000 babies born, on average, 1.5 will have Gaucher disease.
Gaucher disease type 1 is the most common form of the disease, accounting for more than 90% of all cases. It is especially common in those of Ashkenazi Jewish descent, affecting roughly 1 out of every 450 live births in that population.
Worldwide, Gaucher disease type 2 affects about two out of every 1 million live births, while type 3 affects about one out of every 1 million live births. Although Gaucher disease type 3 is rare worldwide, it is especially common in Asian populations, including China, Japan, and India.
Gaucher Disease News is strictly a news and information website about the disease. It does not provide medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
Recent Posts



